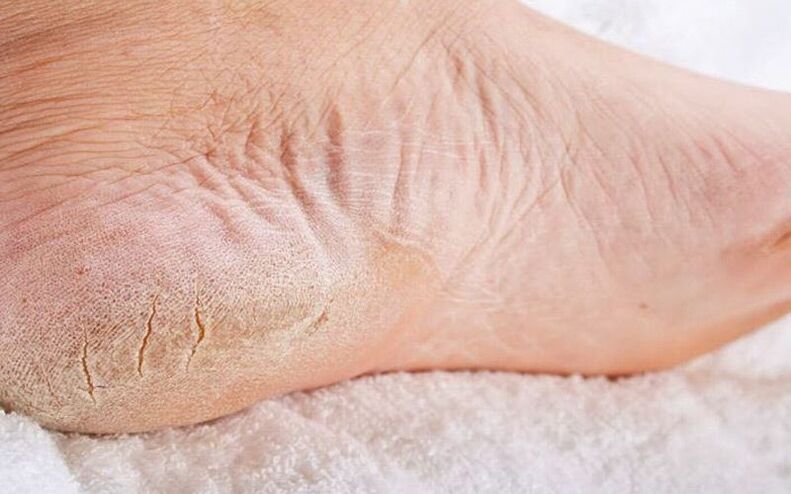
main symptoms of disease
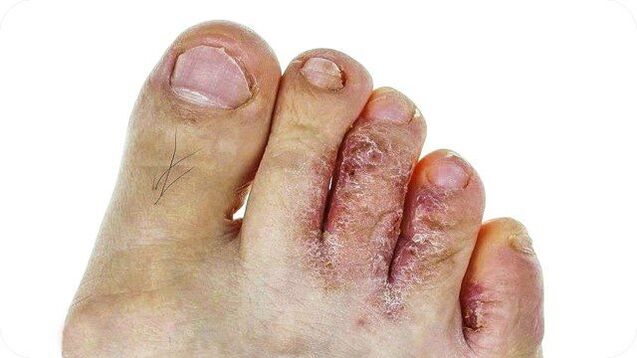
- Characteristic cracks appear between the toes;
- You can tell if fungus is present by the characteristic itching symptoms on your feet and between your toes;
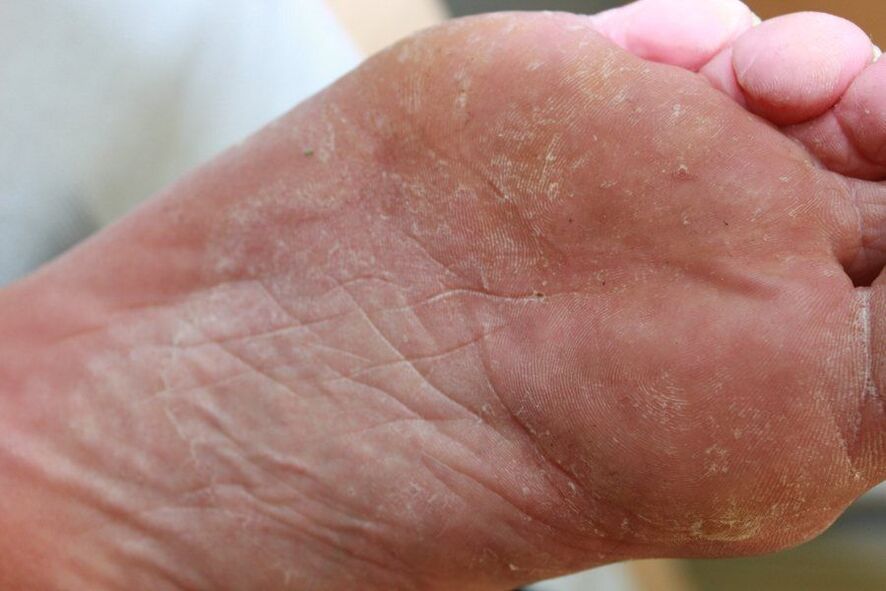
- The skin on the feet is very dry, often flaking and becomes rough;
- Blisters appear between the fingers, which break when damaged;
- Infection may spread to neighboring areas;
- Red spots appear on the skin, causing significant discomfort;
- You can also identify foot fungus by its unpleasant odor.
Signs of fungus depend on the type of pathogen
- If yeast develops on your feet, your nails will gradually thin and fall off their beds. The skin of the feet is congested (red).
- As epidermophyton grows, the nails turn yellow and become speckled. The skin on the feet peels off and gives off a bad odor. A classic symptom of this fungus is that the skin becomes drier.
- When mold appears, the color of your nail plate can suddenly change. If the pathogen gradually spreads throughout the foot, the skin will turn red. The person will suffer from itching and the skin may break out. In this case, pain and other unpleasant sensations occur when walking.
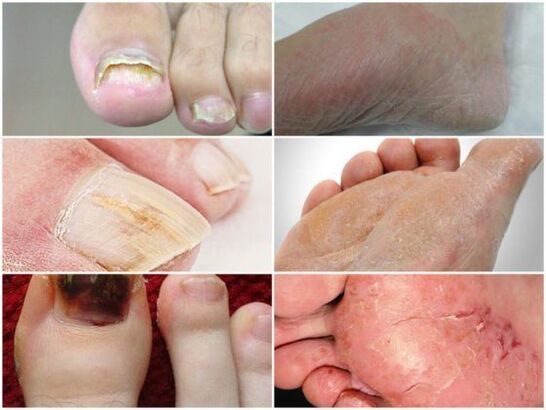
signs of certain forms of fungus
- Interdigital dermatophytosis is the most common stage of the disease. It becomes more active in the spring and summer when your feet sweat the most. Cracks and ulcers appear between the fingers. You can notice scales on their skin. The feet look absolutely healthy. People often feel itchy.
- The erased form looks the least obvious. Visible peeling of skin between fingers. During this stage of the disease, the feet will emit a pungent, unpleasant odor: this appears to be due to increased bacterial activity.
Squamous type
- Thickening of the stratum corneum;
- The skin is shiny and sometimes thickened;
- Patterns on the skin become clearer;
- The fungus gradually spreads to the fingers, entire feet, and affects the nails;
- Sometimes lamellar scales appear on the epidermis;
- The patient does not experience any other unpleasant sensations.
dyshidrosis type
- Bubbles are usually single, but if there are multiple, they merge into one large bubble;
- If left untreated, the fluid in the blister will gradually turn black;
- If a blister bursts, a crust will erode in its place.
intermittent type
Candidiasis of the feet
- The lesion is the third or fourth toe;
- red and swollen skin;
- There is a bubble around the lesion and a layer of skin has fallen off;
- There are pustules and blisters nearby.
Signs of Fungal Nail Infection
- Noticeable change in nail plate color. Depending on the patient's type of pathology, the nails appear in various shades. Sometimes it can only change on part of the deck.
- Nails chipped. It only occurs in advanced stages. If the nail becomes infected at all, it will be destroyed.
- Changes in nail structure.
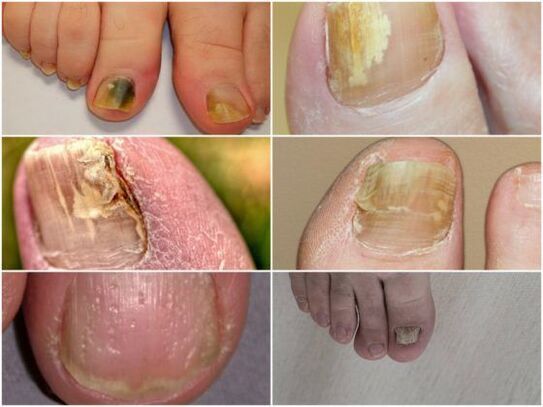
- Shrunk appearance. The nail plate looks very thin. It will darken, sometimes turning grey-brown. The nails gradually peel away from the nail bed. The skin underneath becomes keratinized and becomes loose.
- As the foot fungus takes its normal vegetative form, the plate changes its color. Spots appear on it - white, yellow, green or even black. The structure of the nail is not affected.
- In the hypertrophic form, the plates gradually thicken and become porous. The affected area looks very unsightly and in some cases causes pain when walking. Without treatment, its sides will crumble and collapse.
Certain types of onychomycosis
- Onychomycosis is the most common. A small yellow spot first appears on the free edge of the nail. In the future, you will notice how it increases and the nail plate becomes thicker. People will feel uncomfortable when walking. The spread of unpleasant odors is noticeable. Onychomycosis is difficult to treat.
- Superficial onychomycosis is characterized by damage to only the upper layer of the plate. It won't thicken, but it will become chalk-like over time.
- The rarest form of this disease is subungual onychomycosis. The skin in the nail crease is noticeably thicker. Nails turn white and lose transparency.
General principles of treatment
- Special varnishes, plasters, ointments and sprays are used as soon as signs of fungal infection appear. They must be used consistently and according to instructions.
- If topical treatments are ineffective, complex antifungal drugs are prescribed. They are taken orally.
- Surgery to remove the affected nail.
- Laser Treatment.
- For advanced forms of the disease, systemic drugs are prescribed.
Types of fungal diseases
- Candidiasis - occurs when the body's resistance decreases, most commonly in women;
- Epidermophytosis is an exclusively "male" disease that occurs due to excessive sweating;
- Erythromycosis is a highly contagious disease that can occur even in young children.
Signs and forms of disease
Treatment and best remedies
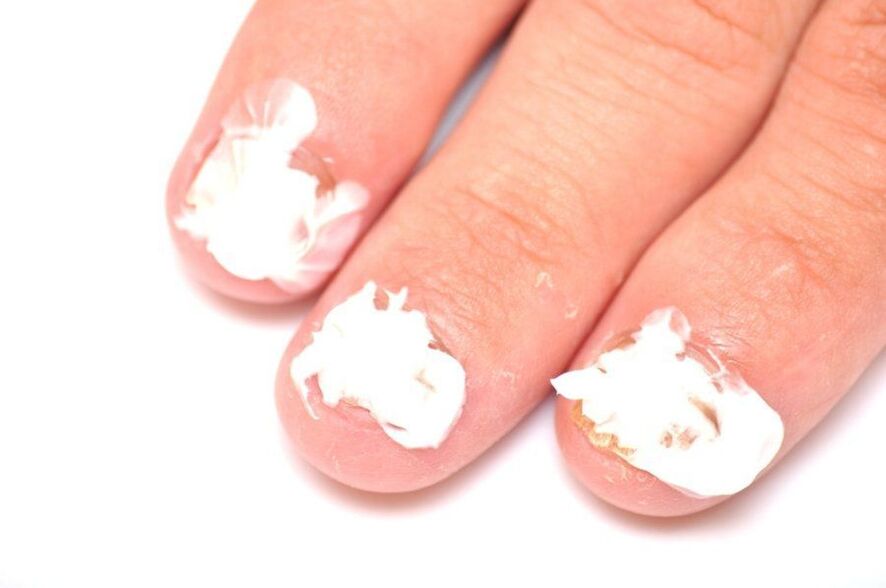

It is recommended to use folk remedies only in the initial stages of the disease and to relieve itching. They must be used with extreme caution as some can burn the skin and may cause burns.
Precaution
- In terms of daily hygiene;
- wear separate shoes (especially in public showers, bathtubs, and swimming pools);
- Regularly treat the inside of shoes with ammonia;
- Change socks every day;
- Enhance and maintain immunity.
Foot Fungus: Symptoms and Treatment, Foot Fungus Photos
Pathogen
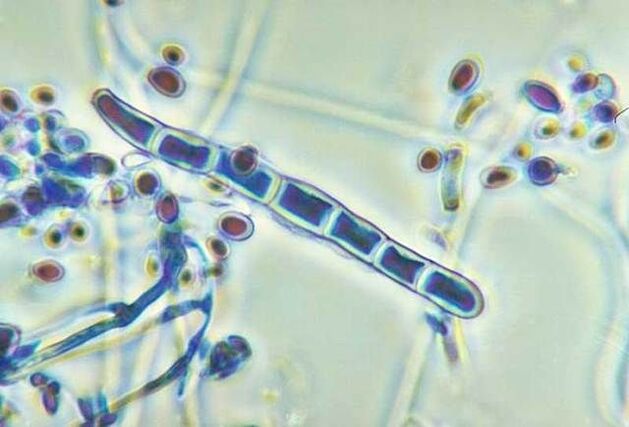
- Trichophyton rubrum,
- Trichophyton mentagrophytes,
- Epidermophyton floccosum.
- Trichophyton dysenterum is the causative agent of fungal disease in children in the United States.
- candida,
- hyaline algae,
- Scytalidium dimidiatum.
Routes of infection and causative factors
- In public places: bathrooms, beach beds, swimming pools, saunas, or even just the beach.
- In households: Shared shoes, lack of separate foot towels, low hygiene standards.
- Habits: exchanging shoes, socks, wearing other people's shoes (for example, wearing the owner's house slippers when visiting).
- Reduced local protection due to circulatory diseases (e. g. , vasculitis, occlusive atherosclerosis of the lower limbs), certain chronic diseases (HIV, other immunodeficiency states, diabetes, etc. ).
- Athletes' feet become sweaty for extended periods of time during long workouts and during the summer when they wear closed or poorly ventilated shoes.
- Cracks and maceration of the skin on the feet.
- miner,
- military personnel,
- bath attendant,
- Regular users of bathhouses and saunas,
- athlete.
disease type
- Interdigital mycosis (dermatophytosis). The most common are the chronic (squamous) or acute (intertriginous) form.
- Plantar mycosis. The most common condition is peeling and keratinization of the skin on the feet.
- Dysphoric dermatophytosis. The formation of bubbles and blisters on the skin of the feet is often reminiscent of allergic dermatitis.
- Deep fungal disease. In this case, not only the surface layer of the skin is affected, but also the deeper layers of the skin.
- Onychomycosis. Fungal toenail infection.
- Athlete's disease caused by Trichophyton.
- Erythrophytosis, caused by Trichophyton rubrum.
Erythroerythema of the Foot: Main Types and Symptoms
symptom
- Squamous (the main symptom is scaly skin),
- Keratinized form - presence of "corns", thickening.
- opreloid,
- Difficulty sweating (blister formation),
- Mixed forms (diaper rash, blisters).
on feet
- Interdigital space: peeling, presence of flour-like scales, small surface cracks.
- There are hardly any complaints or slight itching that may bother you.
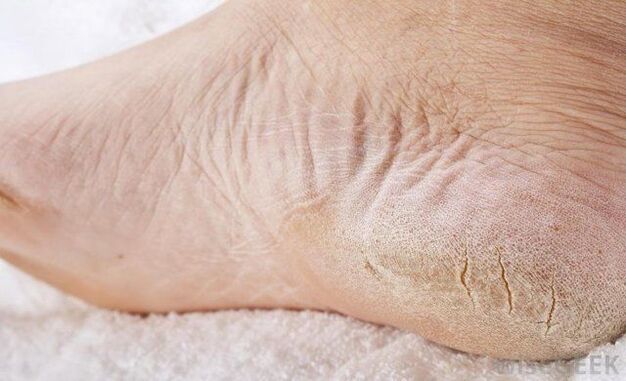
- The skin on the feet is drier,
- Rough skin,
- Rough calluses appear on the soles and outer areas of the feet,
- Deep and painful cracks form in the heel area.
- powdery.The natural folds and wrinkles of the skin appear to be dusted with flour.
- ring. Red spots with edges of sloughed epithelium.
- large layered. In this case, the skin peels off in large patches.
in the space between fingers
on nails
- thicken,
- Tottering,
- Yellowish gray or with brown tint,
- Well-defined white spots then spread throughout the nail.
Complications of erythrophytosis
- Hands - Damage to palms and nails.
- Smooth skin - lesions of the face, inguinofemoral folds, buttocks, legs.
Athlete's foot: types and symptoms
- deleted.
- Keratinization.
- Diaper rash.
- As bubbles form.
- Athlete's nails.
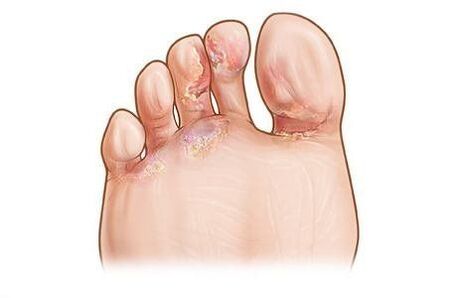
Acute epidermophytosis Podvysotskaya
- Swelling of feet and fingers,
- abundant vesicles,
- The erosion of crying,
- The dipping of the folds between the fingers,
- swollen lymph nodes in the groin,
- Increased body temperature,
- Headache,
- Difficulty walking due to pain,
- Generally weak.
Toenail fungus: symptoms and types
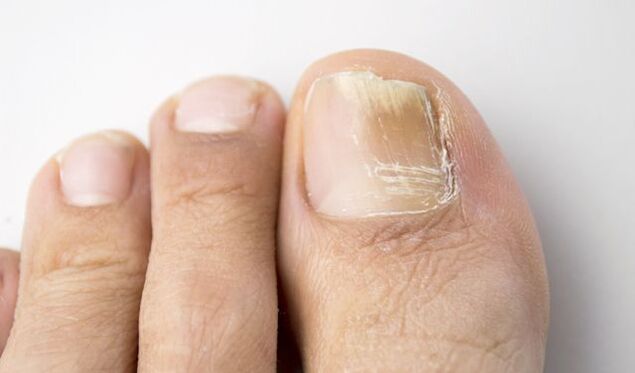
- Discoloration, loss of natural luster,
- Thickening of the nail plate,
- The occurrence of subungual hyperkeratosis,
- Nail damage and nail bed loss.
- Normal nutrition: White and light yellow stripes are visible through the thickness of the nail.
- Atrophic: The nail plate becomes thinner, damaged, and falls off.
Diagnosis of fungal foot infections
- Additional treatment of the material with potassium hydroxide was followed by microscopic examination.
- Wood's lamp inspection.
- The suspected biological material is inoculated onto a special medium for the growth of fungi as well as a medium for bacterial growth.
treat
- Fight against infectious agents. In the initial stages of the disease, topical medications are often prescribed - antifungal ointments, creams, lotions. In severe cases, systemic antifungal drugs are used.
- Improve immunity, improve local blood circulation, and treat underlying diseases.
- Desensitization therapy. Since foot mycosis is often accompanied by allergic reactions, anti-allergic drugs are prescribed accordingly to help improve the patient's condition.
treatment at home
- In order to effectively treat fungal diseases of the feet, it must be remembered that fungi thrive in moist environments. By removing moisture, fungus cannot grow and the chance of cure increases.
- Protect your family from fungal diseases. You should explain to them that from now on you cannot walk barefoot in the apartment, especially in the bathroom or shower. After a bath or shower, the tub itself, trays and floors will need to be treated with a disinfectant.
- Wash your feet daily with soap and use a napkin to collect any loose skin fragments so they don't get under your nails.
- After washing your feet, be sure to dry the spaces between your toes with toilet paper or a hair dryer, then apply an antifungal prescribed by your doctor. Even if the symptoms of fungal disease completely disappear, treatment must continue for several months.
- Use talcum powder when putting on shoes.
- Wear white cotton socks (cleaned daily). Used socks should be boiled or soaked in disinfectant for 10 minutes. Shoes must be disinfected with an antifungal spray.